Fig. 7
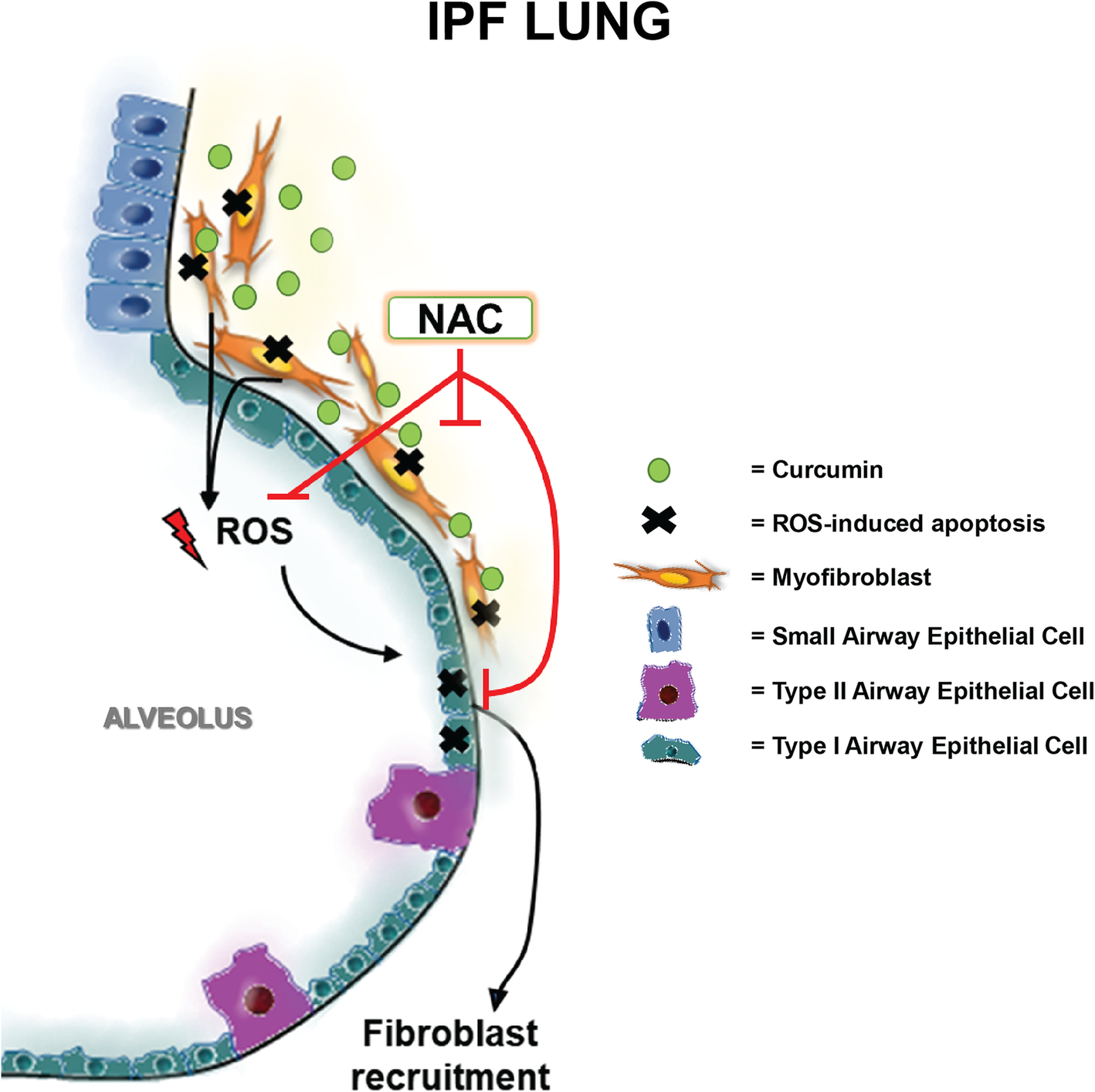
Hypothetical Molecular Model of Curcumin and NAC Co-Treatment in IPF: Curcumin induces ROS mediated apoptosis in myofibroblasts releases excess ROS into the microenvironment. As the IPF lung is an oxidative stress rich environment the excess ROS further damages epithelial cells in the lung. This propagates the wound healing response and may further induce fibrosis in a classical IPF feedforward loop. The introduction of NAC co-treatment attenuates fibroblast apoptosis and alleviates ROS induced oxidative stress in epithelial cells. In turn this prevents additional fibroblast recruitment. Deduction of optimal in-vivo co-treatment concentrations may result in significant antifibrotic potential for therapeutic application
